背景 OpenTSDB + HBase是一个比较常用的时序数据库。因为OpenTSDB长时间不维护,里面遗留着很多问题都没有解决。例如OpenTSDB的查询性能。查询量一增加,OpenTSDB查询就慢。
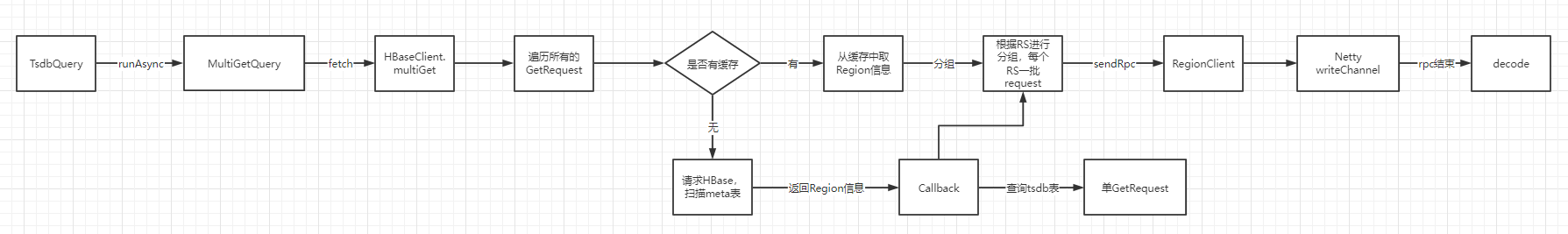
OpenTSDB查询流程 为了解决性能问题,需要阅读OpenTSDB源码。OpenTSDB的查询基本流程图如下:
从流程图上可以看出,tsdb在进行MultiGet查询时,重复发了两遍。在没有缓存的情况下,是串行发送的GetRequest。我们来看下它的调用流程:
TsdbQuery发起查询请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public Deferred<DataPoints[]> runAsync() throws HBaseException { Deferred<DataPoints[]> result = null ; if (this .use_multi_gets && this .override_multi_get) { result = this .findSpansWithMultiGetter().addCallback(new TsdbQuery .GroupByAndAggregateCB()); } else { result = this .findSpans().addCallback(new TsdbQuery .GroupByAndAggregateCB()); } if (this .rollup_usage != null && this .rollup_usage.fallback()) { result.addCallback(new TsdbQuery .FallbackRollupOnEmptyResult()); } return result; }
MultiGetQuery中的fetch逻辑:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private void startFetch () { this .prepareConcurrentMultiGetTasks(); this .fetch_start_time = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) { LOG.debug("Start to fetch data using multiget, there will be " + this .multi_get_wait_cnt + " multigets to call" ); } for (int con_idx = 0 ; con_idx < this .concurrency_multi_get; ++con_idx) { List<MultiGetQuery.MultiGetTask> con_mul_get_tasks = (List)this .multi_get_tasks.get(con_idx); int task_index = ((AtomicInteger)this .multi_get_indexs.get(con_idx)).incrementAndGet(); if (task_index < con_mul_get_tasks.size()) { MultiGetQuery.MultiGetTask task = (MultiGetQuery.MultiGetTask)con_mul_get_tasks.get(task_index); MultiGetQuery.MulGetCB mgcb = new MultiGetQuery .MulGetCB(con_idx, task.getTSUIDs(), task.getGets()); mgcb.fetch(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 private List<Deferred<GetResultOrException>> multiGet (List<GetRequest> requests) { List<Deferred<GetResultOrException>> result_deferreds = new ArrayList (requests.size()); Map<RegionClient, MultiAction> batch_by_region = new HashMap (); for (int i = 0 ; i < requests.size(); ++i) { GetRequest request = (GetRequest)requests.get(i); byte [] table = request.table; byte [] key = request.key; RegionInfo region = this .getRegion(table, key); RegionClient client = null ; if (region != null ) { client = Bytes.equals(region.table(), this .split_meta ? HBASE98_ROOT_REGION : ROOT) ? this .rootregion : (RegionClient)this .region2client.get(region); } if (client != null && client.isAlive()) { request.setRegion(region); MultiAction batch = (MultiAction)batch_by_region.get(client); if (batch == null ) { batch = new MultiAction (); batch_by_region.put(client, batch); } batch.add(request); result_deferreds.add(request.getDeferred().addBoth(MUL_GOT_ONE)); } else { result_deferreds.add(this .sendRpcToRegion(request).addBoth(MUL_GOT_ONE)); } } Iterator var11 = batch_by_region.entrySet().iterator(); while (var11.hasNext()) { Entry<RegionClient, MultiAction> entry = (Entry)var11.next(); MultiAction request = (MultiAction)entry.getValue(); Deferred<Object> d = request.getDeferred(); final class MultiActionCallback implements Callback <Object, Object> { final MultiAction request; public MultiActionCallback (MultiAction request) { this .request = request; } public Object call (Object resp) { if (!(resp instanceof Response)) { if (resp instanceof BatchableRpc) { return null ; } else if (resp instanceof Exception) { return this .handleException((Exception)resp); } else { throw new InvalidResponseException (Response.class, resp); } } else { Response response = (Response)resp; ArrayList<BatchableRpc> batch = this .request.batch(); int n = batch.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { BatchableRpc rpc = (BatchableRpc)batch.get(i); Object r = response.result(i); if (r instanceof RecoverableException) { if (r instanceof NotServingRegionException || r instanceof RegionMovedException || r instanceof RegionServerStoppedException) { try { HBaseClient.this .handleNSRE(rpc, rpc.getRegion().name(), (NotServingRegionException)r); } catch (RuntimeException var9) { HBaseClient.LOG.error("Unexpected exception processing NSRE for RPC " + rpc, var9); rpc.callback(var9); } } } else { rpc.callback(r); } } return null ; } } private Object handleException (Exception e) { } public String toString () { return "multi-action response" ; } } d.addBoth(new MultiActionCallback (request)); ((RegionClient)entry.getKey()).sendRpc(request); } return result_deferreds; }
上面关注的两个点,一个是遍历每个Request时发送的rpc,另一个是打包以后发送的一批rpc。我们先看遍历时,rpc的处理过程。
sendRpcToRegion
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Deferred<Object> sendRpcToRegion (final HBaseRpc request) { if (this .cannotRetryRequest(request)) { return tooManyAttempts(request, (HBaseException)null ); } else { ++request.attempt; byte [] table = request.table; byte [] key = request.key; RegionInfo region = this .getRegion(table, key); if (region != null ) { Deferred d; if (knownToBeNSREd(region)) { NotServingRegionException nsre = new NotServingRegionException ("Region known to be unavailable" , request); d = request.getDeferred(); this .handleNSRE(request, region.name(), nsre); return d; } RegionClient client = this .clientFor(region); if (client != null && client.isAlive()) { request.setRegion(region); d = request.getDeferred(); client.sendRpc(request); return d; } } final class RetryRpc implements Callback <Deferred<Object>, Object> { RetryRpc() { } public Deferred<Object> call (Object arg) { if (arg instanceof NonRecoverableException) { HBaseException e = (NonRecoverableException)arg; if (e instanceof HasFailedRpcException && ((HasFailedRpcException)e).getFailedRpc() != request) { e = ((HBaseException)e).make(e, request); } request.callback(e); return Deferred.fromError((Exception)e); } else { return HBaseClient.this .sendRpcToRegion(request); } } public String toString () { return "retry RPC" ; } } return this .locateRegion(request, table, key).addBothDeferring(new RetryRpc ()); } }
以上时遍历GetRequest时,串行发送的request,当把它处理完之后,会打包进行发生一批request。
RegionClient中,真实发送rpc请求。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 void sendRpc (HBaseRpc rpc) { if (this .chan != null ) { if (rpc instanceof BatchableRpc && !(rpc instanceof GetRequest) && (this .server_version >= 29 || rpc instanceof PutRequest)) { BatchableRpc edit = (BatchableRpc)rpc; if (edit.canBuffer() && this .hbase_client.getFlushInterval() > 0 ) { this .bufferEdit(edit); return ; } this .addSingleEditCallbacks(edit); } else if (rpc instanceof MultiAction) { MultiAction batch = (MultiAction)rpc; if (batch.size() == 1 ) { rpc = this .multiActionToSingleAction(batch); } else { this .hbase_client.num_multi_rpcs.increment(); } } ChannelBuffer serialized = this .encode((HBaseRpc)rpc); if (serialized == null ) { return ; } Channel chan = this .chan; if (chan != null ) { if (this .check_write_status && !chan.isWritable()) { ((HBaseRpc)rpc).callback(new PleaseThrottleException ("Region client [" + this + " ] channel is not writeable." , (HBaseException)null , (HBaseRpc)rpc, ((HBaseRpc)rpc).getDeferred())); this .removeRpc((HBaseRpc)rpc, false ); this .writes_blocked.incrementAndGet(); return ; } ((HBaseRpc)rpc).enqueueTimeout(this ); Channels.write(chan, serialized); this .rpcs_sent.incrementAndGet(); return ; } } boolean tryagain = false ; boolean dead; synchronized (this ) { dead = this .dead; if (this .chan != null ) { tryagain = true ; } else if (!dead) { if (this .pending_rpcs == null ) { this .pending_rpcs = new ArrayList (); } if (this .pending_limit > 0 && this .pending_rpcs.size() >= this .pending_limit) { ((HBaseRpc)rpc).callback(new PleaseThrottleException ("Exceeded the pending RPC limit" , (HBaseException)null , (HBaseRpc)rpc, ((HBaseRpc)rpc).getDeferred())); this .pending_breached.incrementAndGet(); return ; } this .pending_rpcs.add(rpc); } } if (!dead) { if (tryagain) { this .sendRpc((HBaseRpc)rpc); } else { LOG.debug("RPC queued: {}" , rpc); } } else { if (((HBaseRpc)rpc).getRegion() != null && !((HBaseRpc)rpc).failfast()) { this .hbase_client.sendRpcToRegion((HBaseRpc)rpc); } else { ((HBaseRpc)rpc).callback(new ConnectionResetException ((Channel)null )); } } }
OpenTsdb请求处理过程 程序入口:TSDMain.java TSDMain中,执行的是main函数。主要逻辑:
初始化config
创建NIO,ServerBootstrap。用于接收rpc请求。
server设置了一个PipelineFactory,当一个rpc请求被序列化以后,进入rpchandler
初始化TSDB
TSDMain启动时的核心代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { Config config = CliOptions.getConfig(argp); Executor executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); NioServerBossPool boss_pool = new NioServerBossPool (executor, 1 , new BossThreadNamer ()); NioWorkerPool worker_pool = new NioWorkerPool (executor, workers, new WorkerThreadNamer ()); factory = new NioServerSocketChannelFactory (boss_pool, worker_pool); ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap ((ChannelFactory)factory); server.setPipelineFactory(new PipelineFactory (tsdb, manager, connections_limit)); }
在PipelineFactory中,依赖了RpcHandler,当请求被decode以后,进入RpcHandler。核心代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 protected Object decode (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Channel chan, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws Exception { if (buffer.readableBytes() < 1 ) { return null ; } else { int firstbyte = buffer.getUnsignedByte(buffer.readerIndex()); ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.getPipeline(); pipeline.addLast("timeout" , PipelineFactory.this .timeoutHandler); pipeline.remove(this ); pipeline.addLast("handler" , PipelineFactory.this .rpchandler); return buffer.readBytes(buffer.readableBytes()); } }
发起rpc请求 当一个rpc请求进入后,服务端会通过worker线程进行decode,之后进入rpchandler。rpchandler主要用来处理当前发起的http请求。具体方法为:messageReceived
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public void messageReceived (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent msgevent) { Object message = msgevent.getMessage(); if (message instanceof HttpRequest) { this .handleHttpQuery(this .tsdb, msgevent.getChannel(), (HttpRequest)message); } }